April 22nd marks International Earth Day.
Since its conception in 1970, EARTHDAY.ORG has been delivering its mission to diversify, educate and activate the environmental movement worldwide. Today, the organization works with 75,000 partners in 190 countries and has mobilized over 1 billion people to drive positive action for our planet. On April 22nd of every year, this effort culminates in a day of events enabling that social movement.
From its very vision to provide synthetic DNA to improve health and sustainability, Twist Bioscience recognizes the essential role environmental sustainability plays in creating a bright and positive future for our world and all who inhabit it. To mark Earth Day 2021, we highlight a key sustainability initiative at Twist Bioscience - reducing our chemical footprint.
What is a chemical footprint?
Every company has a chemical footprint, defined as the total mass of chemicals used by an event, organization, service, building, or product. Minimizing the use of toxic or environmentally hazardous chemicals throughout supply chains ultimately results in less potentially damaging waste, a safer environment for employees, and a cleaner environment for the world.
Chemicals used in Twist Bioscience’s workflow
At Twist Bioscience, we specialize in DNA synthesis. To generate synthetic DNA, we undertake a reaction called phosphoramidite chemistry. You can read an in-depth description of phosphoramidite chemistry on our blog. There are six main components to this reaction:
- Phosphoramidites - The building blocks of synthetic DNA
- Activator - Activates the new phosphoramidite for addition to the growing DNA strand
- Capper - Blocks off any DNA molecules that did not react as intended in the previous cycle
- Oxidizer - Forms a strong chemical bond between the new base and the growing DNA strand
- Deblocker - Removes protective chemical groups on the phosphoramidite
- Wash - Cleans the growing strand between steps, minimizing unintended reactions
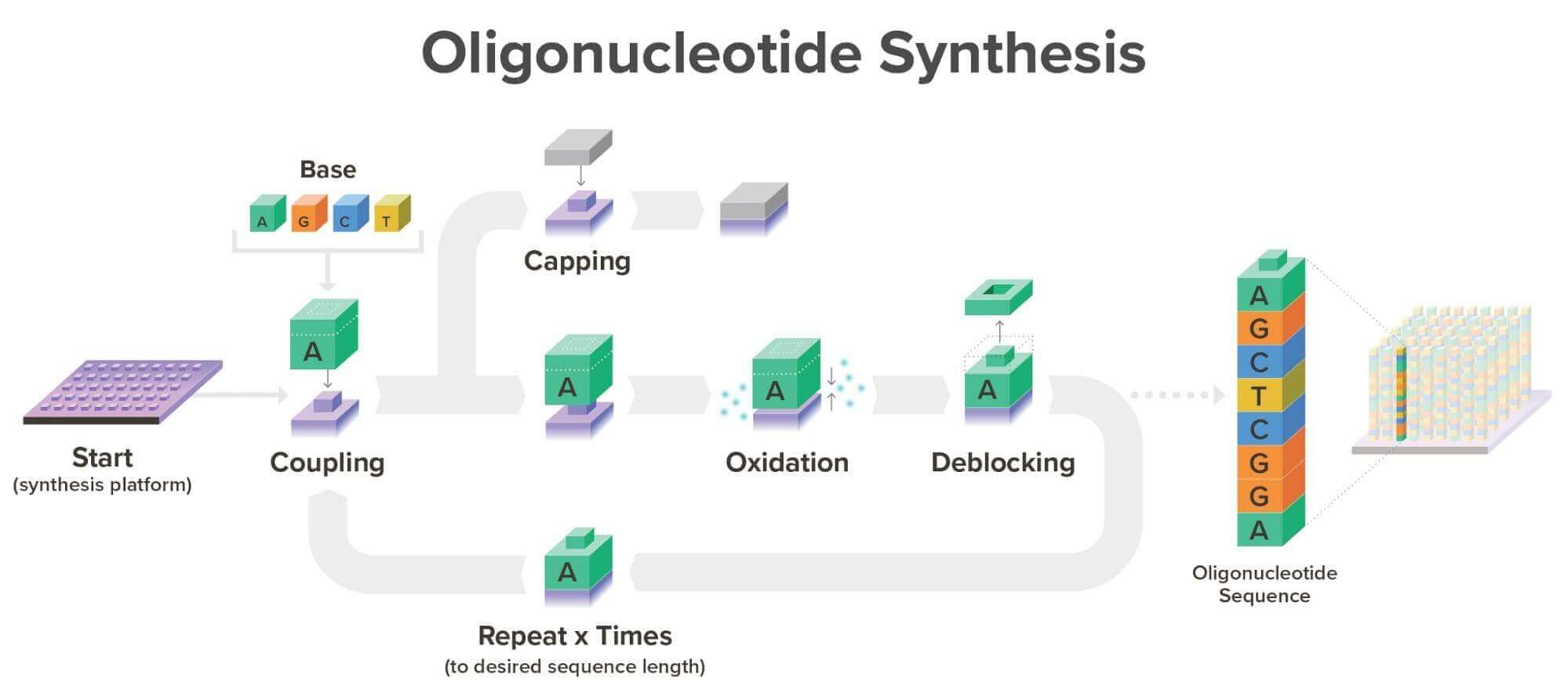
The phosphoramidite reaction has been the gold-standard method for DNA synthesis since its invention almost 40 years ago. DNA synthesis companies use phosphoramidite chemistry to generate oligonucleotides, single-stranded DNA molecules between 20 and 300 base pairs in length. Oligonucleotides see use in various applications, from the synthesis of genes encoding valuable proteins to the formation of target capture panels for efficient next-generation DNA sequencing.
Since its conception, Twist Bioscience has worked to minimize the amount of reagent used in every DNA synthesis reaction. For each gene synthesized, Twist reduces the volume of reagents used by more than 99.8%
Minimizing Twist Bioscience’s chemical footprint
Many DNA synthesis companies synthesize oligos on a 96-well plate, generating 96 oligos in parallel, one in each well. While this process successfully achieves DNA synthesis, it requires high volumes of each reagent. Conversely, Twist Bioscience synthesizes oligos on a silicon plate with the same footprint as a 96-well plate. Each silicon plate contains over 1 million nanometer-scale devices. With the invention and implementation of picoliter-scale fluidic handling, Twist has dramatically miniaturized every step of the synthesis process, including reagent use.
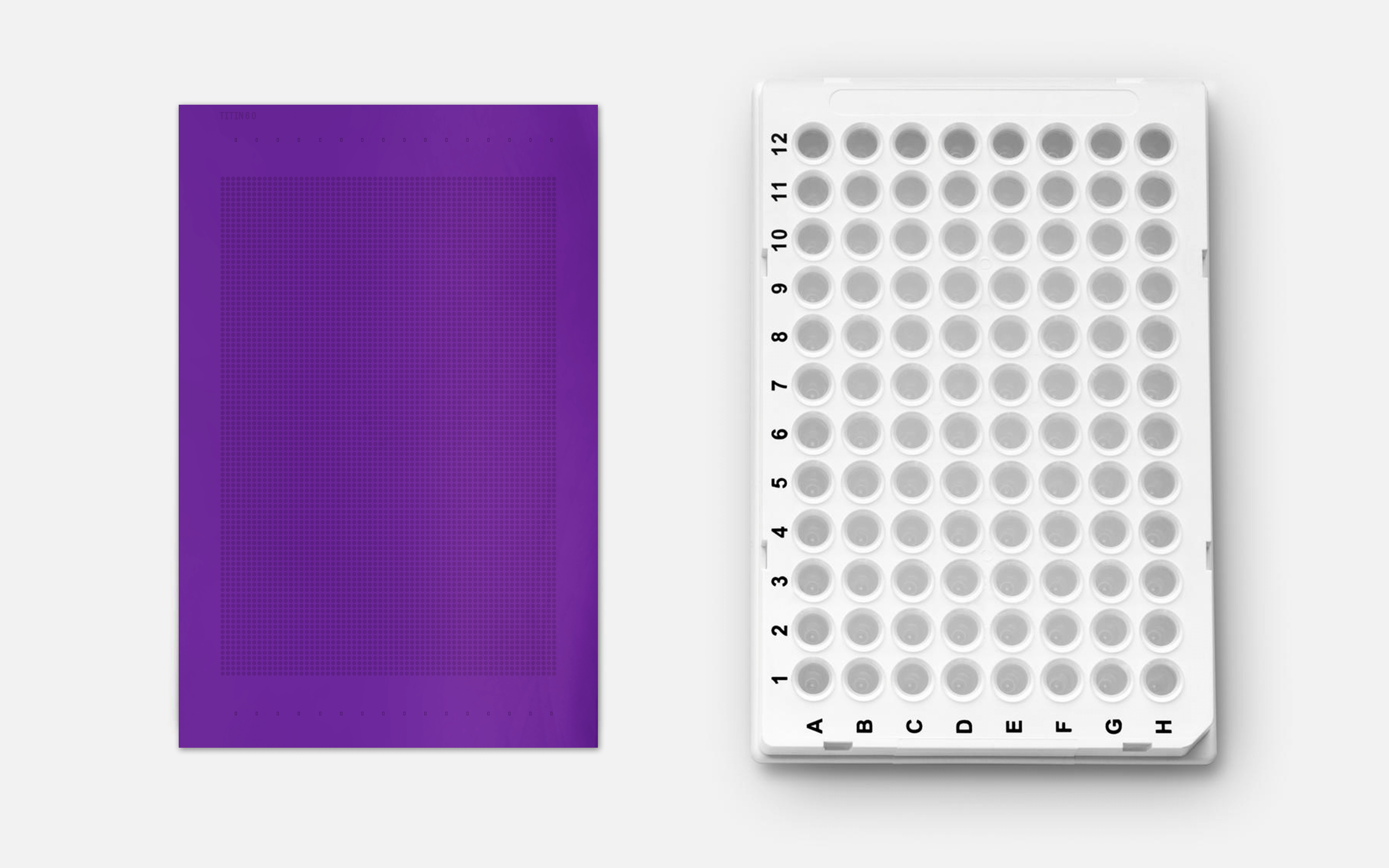
For comparison, let's look at the reagents used to generate two genes using Twist synthesis relative to an industry-standard plate-based oligo synthesizer. We can assume that one gene requires 96 oligos to generate, so one run of a typical 2-plate system will create enough material for two genes.
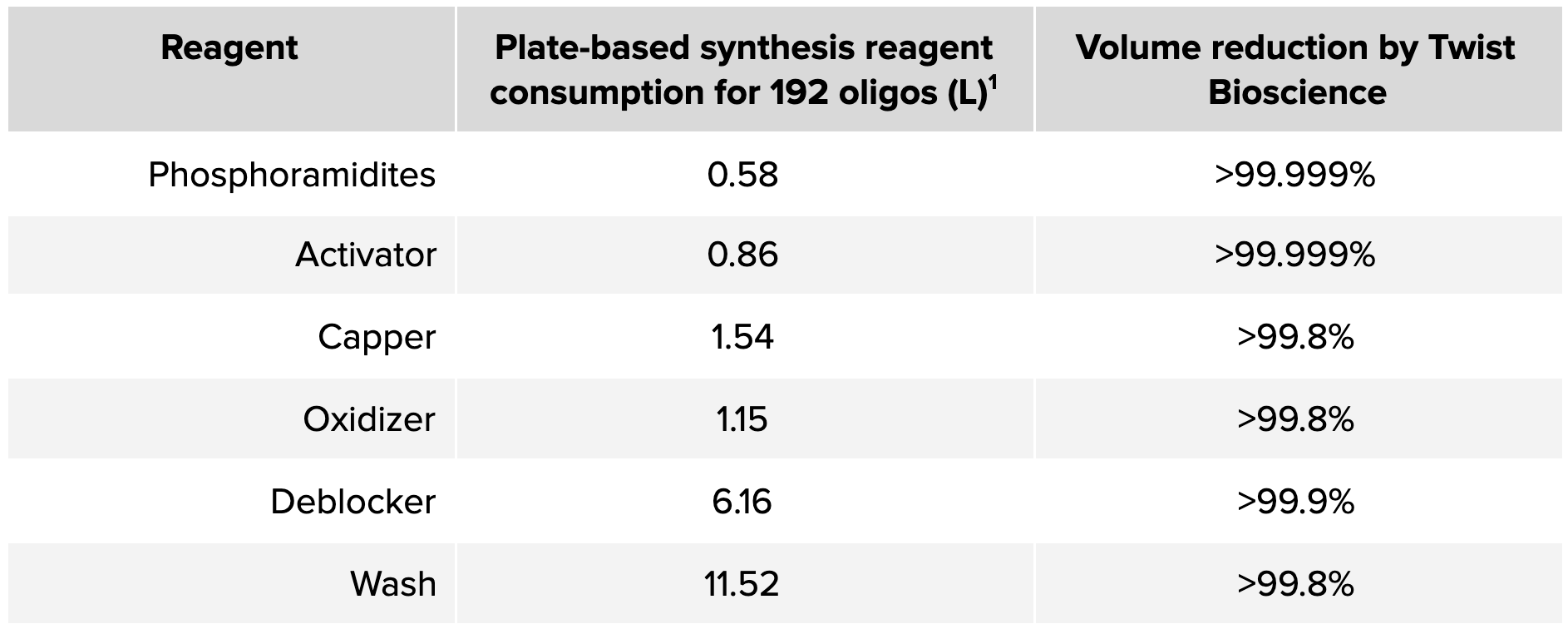
As shown in the example above, Twist Bioscience’s miniaturization of oligo synthesis means at least 99.8% less reagent is used per gene compared to plate-based synthesis, leading to a safer, more environmentally friendly process.
Notably, plate-based synthesizers don’t just lead to wasted reagents but also the wasted product, as they generate around 20x more oligo than is needed for gene synthesis (5 nanomoles generated, 0.25 nanomoles required). On the other hand, Twist Bioscience has a fully integrated process where no excess oligo is produced, completely removing oligo waste from the gene synthesis process.
Twist Bioscience is committed to writing the future of sustainability. We are proud that our customers can make a positive environmental impact by choosing a DNA synthesis process with a reduced chemical footprint. We also believe that every day is earth day. So we are committed to the continued integration of environmental sustainability practices into our business, ensuring Twist Bioscience maintains a positive impact on the world.
To learn more about Modern Global Sustainability and the benefits of synthetic biology at scale, watch our CEO Emily Leproust’s TED talk.
References
- http://www.seaviewsci.com/nblbio/dr_oligo/index.html
Subscribe to our blog
- Terms & Conditions
- Policy on Unsolicited Submissions of Information
- Privacy Policy
- Regulatory and Quality Information
- Security
- Payment Information
-
© 2025 Twist Bioscience. All rights reserved.